Fomalhaut's Dusty Debris Disk
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
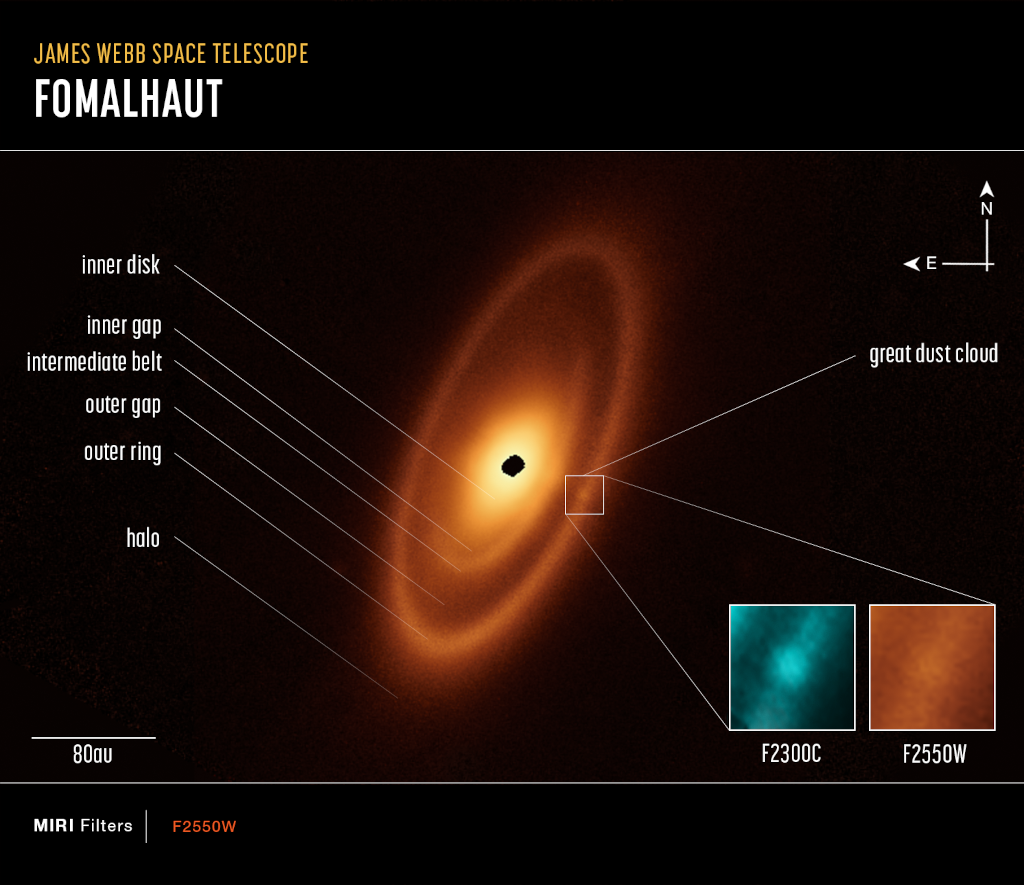
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, Processing: András Gáspár (Univ. of Arizona), Alyssa Pagan (STScI), Science: A. Gáspár (Univ. of Arizona) et al.
Explanation: Fomalhaut is a bright star, a 25 light-year voyage from planet Earth in the direction of the constellation Piscis Austrinus. Astronomers first noticed Fomalhaut's excess infrared emission in the 1980s. Space and ground-based telescopes have since identified the infrared emission's source as a disk of dusty debris, evidence for a planetary system surrounding the hot, young star. But this sharp infrared image from the James Webb Space Telescope's MIRI camera reveals details of Fomalhaut's debris disk never before seen, including a large dust cloud in the outer ring that is possible evidence for colliding bodies, and an inner dust disk and gap likely shaped and maintained by embedded but unseen planets. An image scale bar in au or astronomical units, the average Earth-Sun distance, appears at the lower left. Fomalhaut's outer circumstellar dust ring lies at about twice the distance of our own Solar System's Kuiper Belt of small icy bodies and debris beyond the orbit of Neptune.
Authors & editors:
Robert Nemiroff
(MTU) &
Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman
Specific rights apply.
NASA Web
Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of:
ASD at
NASA /
GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.