Earendel: A Star in the Early Universe
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
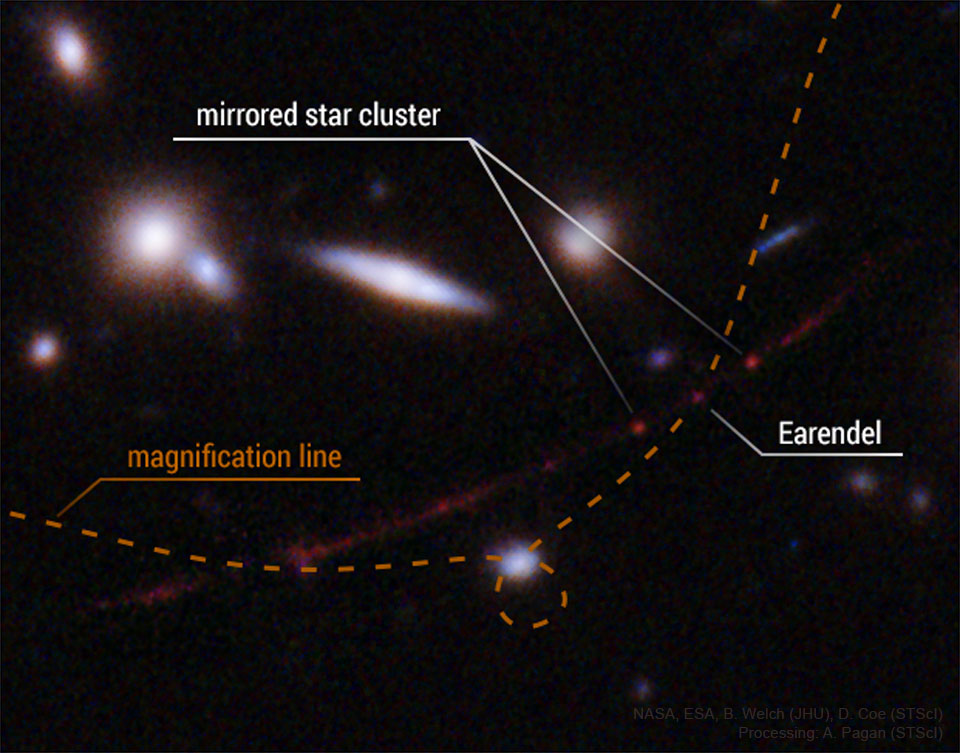
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, B. Welch (JHU), D. Coe (STScI); Processing: A. Pagan (STScI)
Explanation: Is Earendel the farthest star yet discovered? This scientific possibility started when the Hubble Space Telescope observed a huge cluster of galaxies. The gravitational lens effect of this cluster was seen to magnify and distort a galaxy far in the background. This distorted background galaxy -- so far away it has a redshift of 6.2 -- appears in the featured image as a long red string, while beads on that string are likely to be star clusters. The galaxy cluster lens creates a line of maximum magnification line where superposed background objects may appear magnified many thousands of times. On the intersection between the galaxy line and the maximum magnification line is one "bead" which shows evidence of originating from a single bright star in the early universe -- now named Earendel. Future investigations may include more imaging by Hubble to see how Earendel's brightness varies, and, quite possibly, by the new James Webb Space Telescope when it becomes operational later this year. Earendel's great distance exceeds that of any known stable star -- although the star that exploded creating GRB 090423 had a redshift of 8.2.
Authors & editors:
Robert Nemiroff
(MTU) &
Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Phillip Newman
Specific rights apply.
NASA Web
Privacy Policy and Important Notices
A service of:
ASD at
NASA /
GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.